
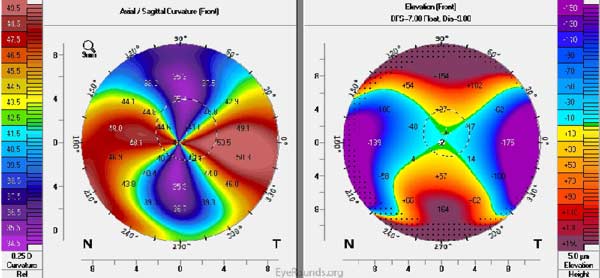
Pellucid marginal degeneration is a bilateral corneal ectasia that results in inferior corneal thinning with a corneal protrusion above the thinnest area. This is in contrast to keratoconus where maximal thinning occurs at the apex of the protrusion.

Ophthalmic Atlas Images by EyeRounds.org, The University of Iowa are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.